Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a bioactive nucleotide that is a precursor to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, crucial for cellular energy production and metabolic processes. Its levels start depleting as we grow older leading to many age-related diseases such as cancer, metabolic disorders, and neurological disorders. According to a study, increased levels of NAD+-consuming enzymes reduced their levels with ageing.
A double-blind, parallel, randomised controlled clinical trial was conducted for safety evaluation at Swasthya Clinic & Research Centre and Nirmaya Hospital in Pune, India. The primary focus of this was to study the anti-ageing effect of Uthever β-NMN for which many factors were taken into consideration, while the secondary focus was to evaluate the safety of this supplement.
Study Design
The clinical trial involved 70 healthy individuals aged between 40-65 years and had BMI between 18.5 and 35 kg/m2. The study adhered to good clinical practice and the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Before enrollment, all subjects were informed about the study's purpose, content, and potential risks, and they voluntarily signed a written informed consent form.
After the screening, 66 participants were randomized with two 150 mg capsules of Uthever NMN supplement or placebo for 60 days. Various factors such as blood cellular NAD+ concentration in serum, 6 min walking endurance test, HOMA- IR Index, and the SF-36 questionnaire were measured to assess how well the supplement boosts NAD+ metabolism in middle-aged and older individuals.
Effect of NMN Supplementation on Blood NAD+ Levels
The NAD+ levels in the blood serum were considered the primary efficacy factor for this study. It was tested by a colorimetric quantification kit from MyBioSource which is based on an enzymatic cycling reaction.
The oral supplement effectively worked as an NAD+ booster as compared to a placebo. At day 30, the group on active supplement showed an 11.3% increase in its levels while no changes were seen in the group administered with placebo. On day 60, there was a further increase in blood NAD+ levels to 38% from baseline in the group on supplement and a 14.3% increase in the placebo group.
As can be observed from the above results of day 30 and day 60, the supplement significantly increases the levels of NAD+ in blood serum.
6 min Walking Endurance Test: Physical Performance and Energy Test
The American Thoracic Society’s 6-minute walk test was the second primary endpoint. It was conducted where the participants' blood oxygen levels were collected by calculating how much distance they covered within 6 mins. On day 30, there was a 4.3% increase in the walking endurance of the participants belonging to the supplemental group and a 3.9% increase in the placebo group, while on day 60 there was a 6.5% rise in the former while later remained at the same level.
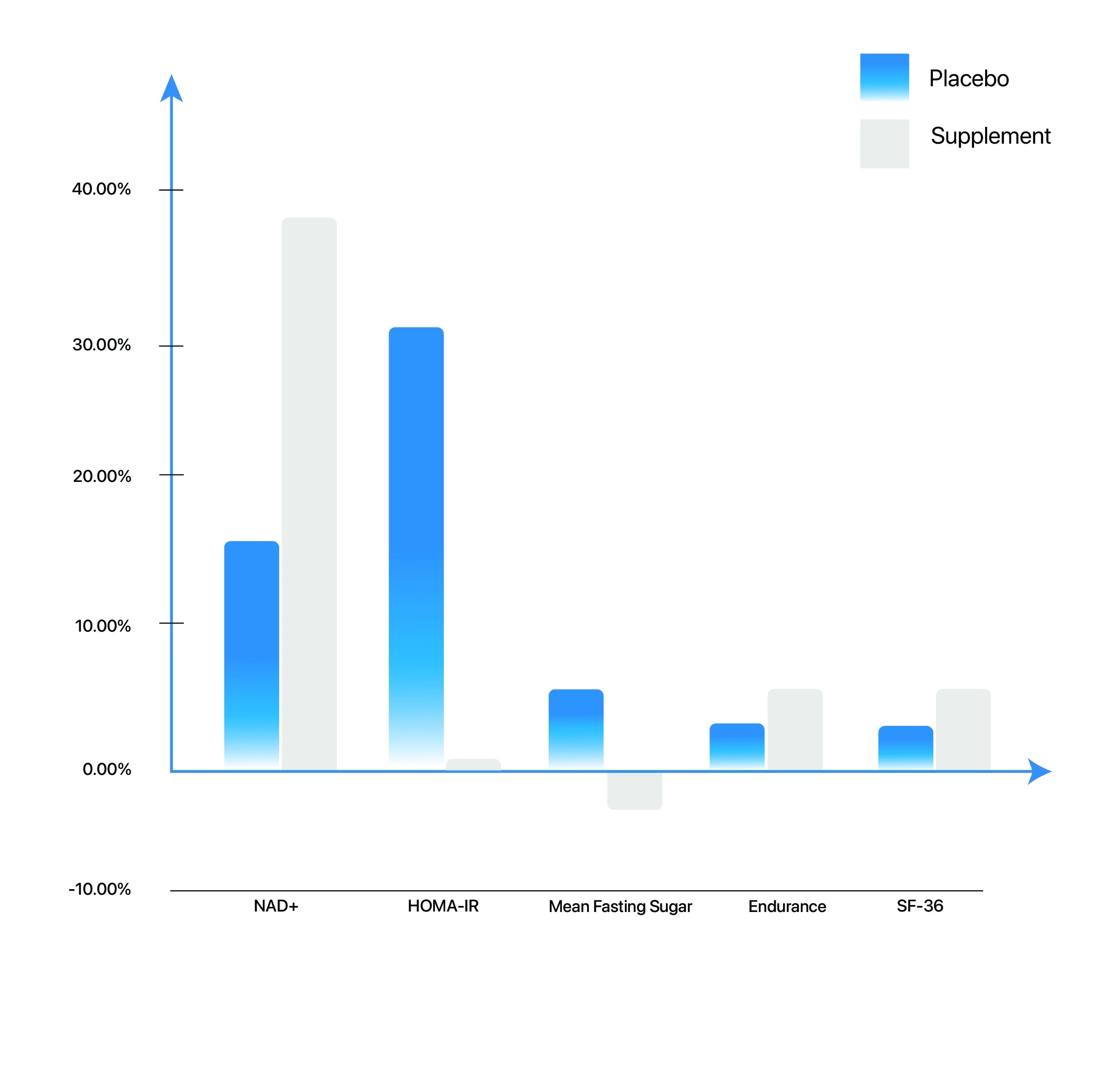
Figure: NMN Supplementation vs Placebo after 2 months of dosage: NAD+ levels increased by 38% from baseline, mean HOMA-IR(Insulin resistance) index was 0.6%, mean fasting sugar levels decreased by 4%, endurance test performance rose by 6.5%, and general health (SF-36) scores increased by 6.5% after two months of supplementation with Uthever β-NMN (300mg)
HOMA-IR: Insulin Sensitivity Test
HOMA IR Index also called Homeostasis Model Assessment - Insulin Resistance, also being an efficacy factor, was calculated by the HOMA2 IR calculator by the University of Oxford Diabetes Trial Unit which was based on fasting insulin levels and fasting blood glucose levels in blood serum. Blood samples from subjects were collected for HOMA after overnight fasting.
The mean HOMA IR Index, at the end of the study, showed a rise of 0.6% among the Uthever group and 30.6% among the placebo group from baseline. Mean Sugar fasting depicted a 4.0% decrease among the supplemental group and a 6.5% increase among the placebo group and mean Serum Insulin fasting showed a 1.9% decrease in the supplemental group with a 26.2% increase among the placebo group.
Similarly, it was observed that the difference in the HOMA IR Index between the Uthever and the placebo groups was not found to be statistically significant.
SF-36: General Health Assessment Test
36-Item Short Form Survey or SF-36 questionnaire was considered as the final efficacy factor to assess improvement in the general health of the participants. In this assessment, participants ae asked 36 questions on energy, emotions, social activities, and physical health for determining their wellbeing (Ware et al., 1992).
On day 30, the SF-36 score increased by 4.0% in the active supplemental group and 3.7% in the placebo group depicting no significant difference. On day 60, the former showed a 6.5% increase and later showed a 3.4% increase. The difference could be observed on day 60 when the SF-36 score doubled for the ones on the active supplement when compared to the placebo group.
Safety and Tolerability of NMN Supplementation
On the last day, safety and organ function tests such as liver function test (LFT) and renal function test (RFT) were done to check for any significant changes in blood or urinary samples along with adverse events in comparison to the placebo. This was conducted to know how safe the supplement was for the participants. The active supplement was considered as safe as there was no clinically meaningful worsening in safety laboratory tests in both groups.
Bottom Line
From the study, it was observed that on day 30 and day 60, the active supplemental group showed an increase in cellular NAD+ levels, enhanced energy levels in participants' walking capacity, and increased general health through higher SF- scores. It may be beneficial to explore higher doses or longer durations of NMN supplementation to enhance this effect.
This study confirms the safety and efficacy of orally administering 300 mg of Uthever β-NMN to healthy individuals. There were no specific harmful effects observed, and adverse events were observed.
This study perfectly served a role in delivering the message that the Decode Age Uthever β-NMN supplement has an anti-ageing effect along with confirming its safety. It also suggests new possibilities for exploring NMN in areas such as reversing ageing and regenerating specific organs, leveraging its anti-ageing and age-reversal effects.
Reference
Huang, H. (2022). A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Parallel Design, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Uthever (NMN Supplement), an Orally Administered Supplementation in Middle Aged and Older Adults. Frontiers in ageing, 3, 851698. https://doi.org/10.3389/fragi.2022.851698
ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories (2002). ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 166(1), 111–117. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.166.1.at1102
Ware, J. E., Jr, & Sherbourne, C. D. (1992). The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical care, 30(6), 473–483.
FAQs
1) What are the benefits of Uthever NMN?
Uthever Beta NMN is scientifically proven to enhance NAD+ levels, offering multiple benefits. It supports graceful ageing, boosts insulin sensitivity and metabolic vitality, improves cognitive function, and aids in DNA repair and cellular functionality.
2) What brand NMN is best?
When it comes to NMN supplements, Decode Age's Uthever® NMN stands out as the best choice. Decode Age uses Uthever NMN which is renowned for its high purity and efficacy, backed by rigorous quality control measures. It's the only clinically validated NMN in the world, ensuring that each dose delivers optimal health benefits safely.
3) Is it OK to take NMN every day?
As evidence says, NMN supplement leads to elevated blood NAD+ levels and is safe and well-tolerated with oral dosages of up to 900 mg daily. The most effective clinical outcomes, as indicated by blood NAD levels and physical performance, are achieved with a daily oral intake of 600 mg.
4) Is NMN anti-ageing?
As people age, their NAD+ levels decrease, resulting in signs of ageing and a slower metabolism. Multiple clinical evidences have shown that NMN supplement stimulates NAD+ production in the body, leading to improved overall health. This includes enhanced cellular function and metabolism, as well as activation of sirtuin enzymes.
5) Why choose Decoge Age NMN over normal NMN?
Decoge Age NMN stands out from regular NMN due to its 99%+ purity, enhanced stability, and rigorous quality checks. As the Decode Age only uses β-NMN which is the active form of NMN with higher bioavailability. These qualities make it more potent and effective, offering superior cellular rejuvenation and longevity benefits compared to normal NMN.
























Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.