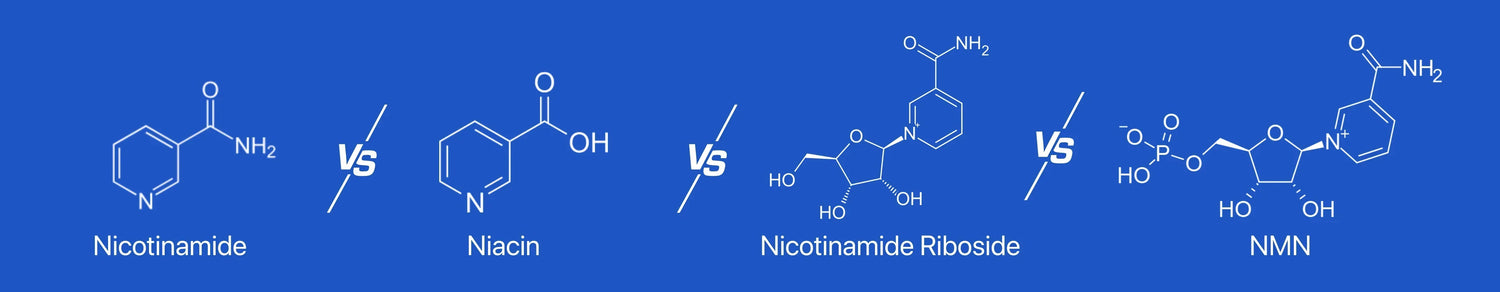
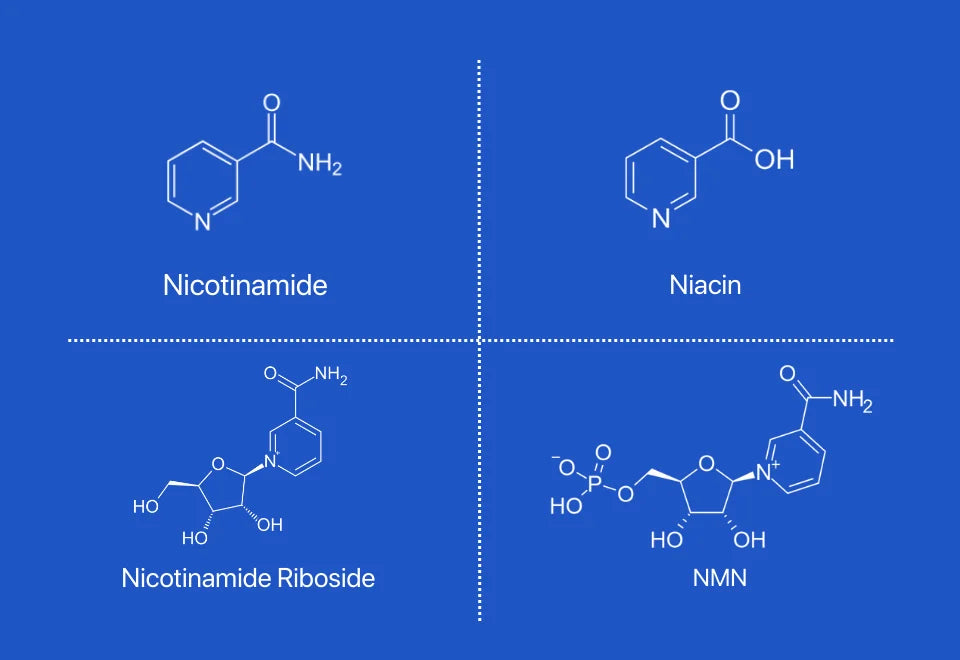
Navigating the world of vitamins and supplements can sometimes feel like deciphering a complex puzzle. Among the many options available, Nicotinamide, Niacin, Nicotinamide Riboside (NR), and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) stand out as crucial players in supporting our health. These compounds, all part of the vitamin B3 family, share commonalities while possessing unique characteristics that set them apart. In this comprehensive guide, we'll use the Feynman Technique to unravel the intricacies of Nicotinamide, Niacin, Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN, shedding light on their differences and their potential impact on our well-being.
What is Niacin?
Niacin, also referred to as nicotinic acid, is another form of vitamin B3. Niacin is vital for converting food into energy and supporting various cellular processes. However, niacin can cause a temporary "niacin flush." This flush is characterized by a warm, tingling sensation and reddening of the skin, which occurs due to the widening of blood vessels.
Niacin as Vitamin B3:
Niacin is an essential component of the coenzymes NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate). These coenzymes play a central role in cellular metabolism, helping enzymes carry out reactions that are vital for energy production, DNA repair, and other essential functions.
Niacin's Role in Health:
Cholesterol Management:
Niacin has been used to improve cholesterol levels. It can increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol while lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides.
Cardiovascular Health:
By positively affecting cholesterol levels, niacin contributes to overall heart health. However, it's important to note that niacin supplementation should be done under medical supervision due to potential side effects.
Brain Function:
Adequate niacin intake is essential for maintaining proper brain function and cognitive health. Niacin deficiency has been linked to cognitive impairment and an increased risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
What is Nicotinamide (Niacinamide)?
Nicotinamide is a form of vitamin B3. Nicotinamide plays a crucial role in converting food into energy and supporting various enzymatic reactions in the body. Unlike niacin, nicotinamide doesn't cause the characteristic "niacin flush," a temporary reddening of the skin often accompanied by a tingling sensation.
Benefits of Nicotinamide:
Skin Health:
Nicotinamide is renowned for its benefits in maintaining healthy skin. It has anti-inflammatory properties that can help manage conditions like acne, eczema, and rosacea. Additionally, it assists in maintaining the skin's barrier function, preventing moisture loss and promoting a supple complexion.
Cellular Protection:
Nicotinamide acts as an antioxidant, helping to neutralize harmful free radicals that can damage cells and DNA. This cellular protection is essential for overall health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Gut Health:
Nicotinamide also plays a role in maintaining a healthy gut. It supports the integrity of the gastrointestinal tract's lining, which is crucial for preventing leaky gut syndrome and other digestive issues.
Nicotinamide also plays a role in maintaining a healthy gut. It supports the integrity of the gastrointestinal tract's lining, which is crucial for preventing leaky gut syndrome and other digestive issues.
Nicotinamide vs Niacinamide: Are They the Same?
Yes — nicotinamide and niacinamide are the same compound. They're just two names for the amide form of vitamin B3.
Why Two Names?
- Nicotinamide is the scientific name often used in research and supplements.
- Niacinamide is more common in cosmetics and skincare products.
So, if you’re using a serum with niacinamide and reading a study about nicotinamide, you’re dealing with the exact same molecule.
Nicotinamide vs Niacin: What’s the Difference?
Both are forms of vitamin B3, but they behave quite differently.
|
Feature |
Nicotinamide |
Niacin (Nicotinic Acid) |
|
Flush? |
No flush |
Yes (can cause skin flushing) |
|
Used for |
Skin health, NAD+ support, cell repair |
Cholesterol management, NAD+ support |
|
Side Effects |
Generally well tolerated |
Flushing, itching, possible liver effects at high doses |
|
Common in |
Supplements, skincare |
Prescription meds for cholesterol |
Niacin has a longer history in cardiovascular care, but many people avoid it due to the uncomfortable flush it causes at therapeutic doses.
What is Nicotinamide Riboside (NR)?
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a relatively new player in the vitamin B3 arena. It's a precursor to NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and has garnered attention for its potential to boost NAD+ levels in the body.
NR's Impact on NAD+ Levels:
NAD+ is a coenzyme that plays a critical role in various cellular processes, including energy production and DNA repair. As we age, NAD+ levels tend to decline, which can impact overall health. NR has been studied for its ability to increase NAD+ levels, potentially mitigating some age-related health issues.
Potential Benefits of NR:
Mitochondrial Function:
NAD+ is involved in energy production within cells, particularly in the mitochondria. By supporting NAD+ levels, NR could enhance mitochondrial function and overall cellular energy production.
Anti-Ageing Effects:
Some research suggests that increasing NAD+ levels through NR supplementation might have anti-aging effects. NAD+ is involved in DNA repair and maintenance, which are crucial for slowing down the ageing process.
Metabolic Health:
NR's impact on NAD+ levels could also influence metabolic health. It might help regulate glucose and lipid metabolism, potentially benefiting individuals with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
What is NMN?
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a bioactive nucleotide that is derived from ribose and nicotinamide. It's one of the key compounds in the body that plays a role in the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), an essential coenzyme in cells that is involved in cellular metabolism, DNA repair, and other vital cellular processes.
NAD+ levels are known to decline with age, and this decline is associated with various age-related health issues. Because NMN is a direct precursor to NAD+, it has garnered significant attention in the fields of aging research and nutritional science as a potential molecule to boost NAD+ levels and thereby potentially counteract certain age-related declines in cellular function.
Potential benefits of NMN:
The unique attributes of NMN have prompted researchers to explore its potential applications. Studies have indicated that NMN supplementation might have positive effects on age-related issues, metabolic function, and cardiovascular health. NMN's ability to enhance NAD+ levels could contribute to improved cellular health and may even play a role in extending lifespan. However, it's essential to note that while the initial findings are promising, further research is required to fully understand the extent of NMN's benefits.
NR vs NMN: Which is Better for Longevity?
Both Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) are NAD+ precursors. They’ve become some of the most talked-about and sought-after ingredients in the anti-ageing world but they differ in structure and function.
|
Feature |
NR |
NMN |
|
Structure |
Nicotinamide + Ribose |
NR + Phosphate group |
|
Pathway to NAD+ |
Converts to NMN → NAD+ |
Converts directly to NAD+ |
|
Bioavailability |
Moderate |
High (especially with new delivery tech) |
|
Research Focus |
Mitochondrial health, metabolism |
Longevity, anti-ageing, cognition |
|
Cost |
Moderate to high |
High |
NMN is often regarded as slightly more efficient, especially in older individuals, due to better cell uptake and bioavailability but human studies are still ongoing.
Comparative Analysis of Nicotinamide, Niacin, Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN
Nicotinamide is an amide derivative of Vitamin B3. On the other hand, Niacin represents Vitamin B3 itself and is distinguished by its carboxyl group. NR, or Nicotinamide Riboside, is a compound where Nicotinamide is coupled with ribose. Meanwhile, NMN, which stands for Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, is structurally similar to NR but has an additional phosphate group.
Differences/Similarities between Nicotinamide, Niacin, Nicotinamide Riboside, and NMN
|
Feature/Aspect |
Nicotinamide |
Niacin |
NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) |
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) |
|
Туре |
Vitamin B3 derivative |
Vitamin B3 |
Vitamin B3 derivative |
Vitamin B3 derivative |
|
Contribution to NAD+ Synthesis |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Role in Metabolism |
Participates in redox reactions |
Participates in redox reactions |
Participates in redox reactions |
Participates in redox reactions |
|
Conversion to NAD+ |
Direct |
Requires conversion to NMN and then NAD+ |
Converts to NMN and then to NAD+ |
Directly converts to NAD+ |
|
Bioavailability |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Moderate |
High (Best) |
|
Common Uses |
Commonly found in multivitamins, B-complex supplements, and skincare products |
Often prescribed at higher doses for its ability to positively affect cholesterol profiles |
Promoted for anti-ageing benefits due to its potential to boost NAD+ levels in the body. |
Used in anti-ageing and longevity research for its potential to enhance NAD+ levels. |
|
Side Effects |
Possible at high doses |
Flushing. itching at high doses |
Well-tolerated |
Well-tolerated |
Choosing the Best Vitamin B3 Supplement: Considerations and Options
When considering vitamin B3 supplements, several factors come into play. Understanding the available options and your specific health goals is crucial in making an informed decision.
Why NMN is considered the best vitamin B3 Supplement
NMN is often regarded as having a higher bioavailability. This means that NMN can be more efficiently absorbed by the body, potentially leading to faster and more pronounced effects on NAD+ levels. However, the choice between NMN and other B3 supplements should be based on individual health goals and consultation with a healthcare provider.
Remember, while supplements can offer remarkable benefits, a holistic approach to health, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, remains the foundation for a thriving lifestyle.
In conclusion, while nicotinamide, niacin, and nicotinamide riboside each have their merits, NMN emerges as a standout contender, especially when it comes to enhancing gut health and cellular resilience. Its distinct pathway to NAD+ synthesis, potential longevity benefits, and broader applications make NMN a compelling choice for those seeking to optimize their health span. As you embark on your journey towards improved well-being, consider the promising potential of NMN as a partner in your quest for vitality and longevity.


























Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.