Urolithin A (UA) is a compound that helps your cells clean out damaged mitochondria through a process called mitophagy. Healthy mitochondria are essential for energy production and can impact how well you age. Here's what you need to know:
- What It Does: UA improves mitophagy, which recycles damaged mitochondria, boosting energy and muscle health.
- How It Works: Activates key pathways (like PINK1/Parkin) to clear out dysfunctional mitochondria, supporting cellular health.
- Benefits: Studies show UA can increase muscle strength by 10–12%, improve endurance, and reduce inflammation.
- Sources: Found indirectly in foods like pomegranates, walnuts, and berries, but only 30–40% of people naturally produce it due to gut bacteria differences.
- Supplementation: Taking 250–1,000 mg of UA daily is more effective than relying on food sources.
UA is a promising option for improving mitochondrial health and combating ageing-related issues like muscle decline and inflammation. Clinical trials in humans and animals highlight its potential to support longevity and overall health.
Urolithin A and Mitophagy Basics
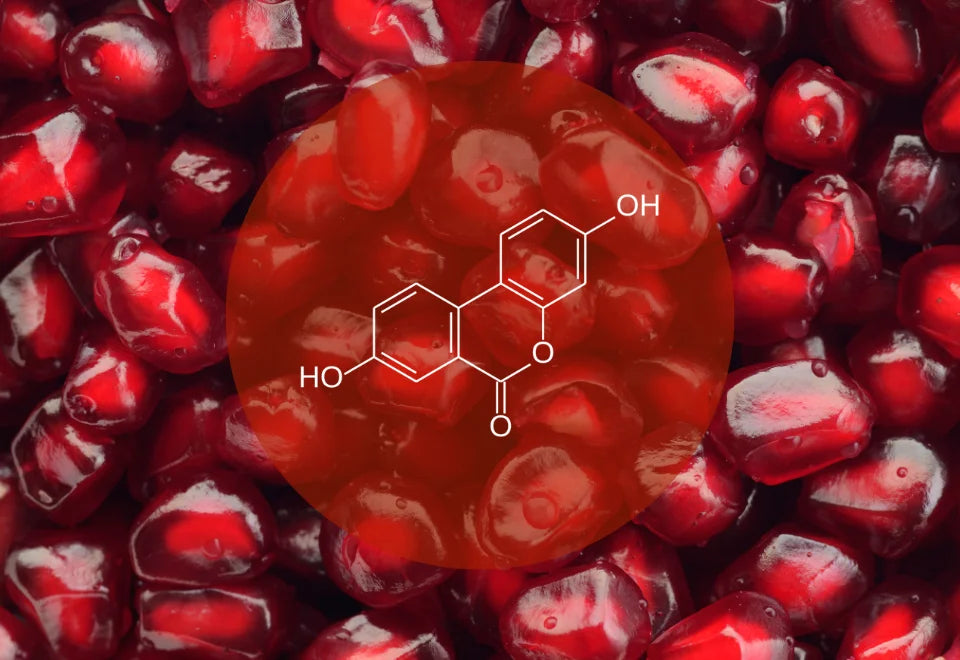
What is Urolithin A?
Urolithin A (UA) is a compound created in the body when gut bacteria process ellagitannins - substances found in foods like pomegranates, walnuts, and certain berries. It’s important to note that UA itself isn’t found in these foods; instead, your gut bacteria are responsible for converting ellagitannins into UA. However, this conversion doesn’t happen for everyone. Only about 30–40% of people naturally produce UA, and this depends on the makeup of their gut microbiome. Now, let’s take a closer look at mitophagy, the process that helps recycle damaged mitochondria in our cells.
How Mitophagy Works
Mitophagy, the cellular process of clearing out damaged mitochondria, unfolds in three main steps:
-
Detection Phase
Proteins such as PINK1 and Parkin identify mitochondria that aren’t functioning properly [1]. -
Isolation Phase
The damaged mitochondria are surrounded by a double membrane, preparing them for removal. -
Elimination Phase
These enclosed mitochondria are sent to lysosomes, where they are broken down and recycled [1].
This process keeps cells running efficiently by maintaining energy production. It also plays a role in longevity, as we’ll explore next.
Mitophagy's Effects on Lifespan
Effective mitophagy supports energy production at the cellular level and has been linked to longer lifespans. Research in animals has shown that boosting mitophagy with Urolithin A can lead to striking results:
- A 57% rise in spontaneous activity in older mice [2].
- A 9% improvement in muscle strength in ageing mice [2].
- Longer lifespans observed in experimental models [3].
Human trials have also shown encouraging results. For example:
- A 20% increase in muscle fatigue resistance after just two months [3].
- A 10–12% improvement in leg muscle strength among middle-aged adults [3].
Urolithin A's Role in Mitophagy
How Urolithin A Works
Urolithin A (UA) helps initiate mitophagy by activating AMPK, suppressing mTOR, and boosting the PINK1/Parkin pathway.
A study in 2021 showed that giving UA at 50 mg/kg/day to Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) mice improved the removal of damaged mitochondria [3].
"UA improves muscle function by inducing mitophagy in muscular dystrophy." – Luan et al [3].
These processes play a key role in UA's ability to improve energy production, as explained below.
Effects on Cell Energy
UA supports cellular energy by clearing out damaged mitochondria and maintaining healthy ones.
A 2023 study examined UA's impact on a mouse model of obesity-related metabolic cardiomyopathy [4]. Mice treated with 50 mg/kg/day of UA for four weeks showed clear benefits:
| Parameter | Observed Effect |
|---|---|
| Mitophagy Activity | Increased pathway activation |
| Mitochondrial Function | Greater energy production efficiency |
| Metabolic Health | Reduced signs of cardiomyopathy |
Another study found that middle-aged adults taking 500 mg of UA daily experienced:
- A 12% boost in hamstring muscle strength
- A 15% increase in total cycling distance
- Lower C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, reflecting reduced systemic inflammation
These results underscore UA's potential to support cellular health and combat ageing-related issues. Its ability to enhance mitophagy and decrease inflammation makes it a promising option for addressing cellular decline [5].
Research on Urolithin A and Longevity
Results from Animal Studies
Animal studies suggest that Urolithin A (UA) can extend lifespan and enhance mitochondrial function. A 2016 study found that UA supplementation in C. elegans increased lifespan by up to 45.4%, alongside better mitochondrial performance and cellular health.
Rodent studies also demonstrated improvements in physical performance after UA supplementation:
| Animal Model | Treatment Duration | Performance Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Mice | 8 weeks | 57% more spontaneous exercise and a 9% boost in grip strength |
| Wistar Rats | 6 weeks | 65% increase in running capacity |
These findings in animals have paved the way for further exploration in humans.
Human Research Results
Clinical trials have shown that UA can counteract muscle decline linked to ageing. Building on the success of animal studies, a review of five clinical studies involving 250 participants found that daily UA supplementation (10–1,000 mg) led to dose-dependent anti-inflammatory effects within 28 days to 4 months [6].
One notable double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (March 2018–July 2020) studied the effects of 1,000 mg of UA daily in adults aged 65–90 years. The results revealed significant gains in muscle endurance, as illustrated below:
| Measurement | UA Group | Placebo Group |
|---|---|---|
| FDI Muscle Endurance | 95.3 contractions | 11.6 contractions |
| TA Muscle Endurance | 41.4 contractions | 5.7 contractions |
| 6-Minute Walk Distance | 60.8 meters | 42.5 meters |
Participants taking UA also showed reduced plasma levels of acylcarnitines, ceramides, and C-reactive protein - indicators of better metabolic health and lower inflammation [7].
These combined findings from animal and human studies highlight UA's potential to support healthy ageing by improving mitophagy and overall cellular function.
sbb-itb-55c436e
Using Urolithin A
Many people naturally produce very little Urolithin A, making supplementation an effective way to support mitochondrial health.
Natural Sources
Urolithin A itself isn’t found in food, but certain foods contain ellagitannins, which gut bacteria can convert into Urolithin A. Check out these top sources:
| Food | Ellagic Acid Content |
|---|---|
| Pomegranate Extract | 250–900 mg/100 g |
| Walnuts | 750 mg/100 g |
| Raspberries | 65 mg/100 g |
| Strawberries | 22.3 mg/100 g |
| Almonds | 54.7 mg/100 g |
Supplement Guide
Research suggests these dosage guidelines:
- Daily dosage: 250–1,000 mg.
- Consistency: Regular daily use is essential for the best results.
Taking Urolithin A as a direct supplement provides about six times better absorption compared to getting it from food. Experts recommend starting supplementation in your 30s or 40s to promote long-term cellular health. For a tailored plan, consider advanced testing services.
Summary
Urolithin A (UA) stands out for its ability to boost mitophagy, a process that clears out damaged mitochondria, leading to better cellular health and longevity. Clinical studies across various species, including humans, show that UA can improve muscle strength, endurance, and reduce inflammation - all thanks to its targeted activation of mitophagy.
What makes UA unique is its focused method of supporting cellular health. Unlike compounds that broadly stimulate autophagy, UA specifically enhances mitophagy without significantly affecting mTOR. This ensures that cellular energy production remains steady while oxidative stress is reduced.
Beyond muscle health, research suggests UA may help protect against age-related issues like cognitive decline, joint problems, and metabolic disorders [8]. The US FDA has classified UA as "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) for daily doses ranging from 250 mg to 1,000 mg.
FAQs
What is Urolithin A (UA)?
Urolithin A is a compound produced when gut bacteria break down ellagitannins found in foods like pomegranates, walnuts, and berries. It enhances mitophagy, helping cells remove damaged mitochondria for better energy production and longevity.
How does Urolithin A support mitophagy?
UA activates key cellular pathways, including PINK1/Parkin and AMPK, which help identify, isolate, and remove dysfunctional mitochondria. This process improves mitochondrial function and cellular energy.
What are the benefits of Urolithin A supplementation?
- Muscle Strength & Endurance: Studies show a 10–12% improvement in muscle strength and a 15% increase in endurance.
- Reduced Inflammation: Lower C-reactive protein (CRP) levels indicate reduced systemic inflammation.
- Enhanced Mitochondrial Function: Helps maintain energy production and metabolic health.
- Longevity Potential: Animal studies suggest UA can extend lifespan and improve physical activity levels.
Can I get Urolithin A from food?
Not directly. UA is produced when gut bacteria convert ellagitannins found in foods like pomegranates, walnuts, and berries. However, only 30–40% of people have the gut bacteria needed to produce UA naturally.



























1 comment
Santosh Iyer
When will DecodeAge start selling Urolithin A?
Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.